Unifying Retrieval and Generation, Reasoning-Driven Cold-Start Recommendation with LLMs and More!
Vol.132 for Nov 24 - Nov 30, 2025
Stay Ahead of the Curve with the Latest Advancements and Discoveries in Information Retrieval.
This week’s newsletter highlights the following research:
Unifying Retrieval and Generation through Continuous Latent Representations, from Apple
Reasoning-Driven Cold-Start Recommendation with LLMs, from Netflix
Accelerating Vector Database Retrieval Through Adaptive Multi-Resolution Indexing, from Liu et al.
Latent Semantic Routing for Parameter-Efficient Domain Specialization in Decoder-Only Rerankers, from Wang et al.
Rediscovering Feedback Models in the Era of LLM-Based Query Expansion, from the University of Waterloo
A Lightweight End-to-End Model for Structured Document Understanding, from NVIDIA
Efficient Vision-Language Document Retrieval via Pyramid Indexing and Semantic Fusion, from Inception AI
Generative Early Stage Ranking with Target-Aware Attention at Scale, from Meta
An End-to-End Joint Training Framework for Graph Neural Networks and Recommender Systems, from TikTok
Addressing Feature Heterogeneity and Sparsity in Industrial Recommenders, from Alibaba
[1] CLaRa: Bridging Retrieval and Generation with Continuous Latent Reasoning
This paper from Apple presents CLaRa (Continuous Latent Reasoning), which unifies retrieval and generation through shared continuous document representations. Traditional RAG systems suffer from separate optimization of retrieval and generation modules, creating architectural mismatches where retrievers operate on embeddings while generators consume raw text. The authors propose a two-stage framework: first, SCP (Salient Compressor Pretraining) trains a compressor using synthetically generated QA pairs and paraphrases to create semantically rich compressed representations; second, CLaRa performs end-to-end joint training of a query reasoner and generator using only next-token prediction loss. This design allows gradients to flow from the generator back to the retriever without requiring explicit relevance labels. The compressed representations serve dual purposes: enabling efficient similarity-based retrieval and directly feeding into generation, while drastically reducing context length (achieving 4-128x compression). Experiments across NQ, HotpotQA, MuSiQue, and 2WikiMultihopQA demonstrate that CLaRa achieves state-of-the-art compression and reranking performance, often surpassing text-based baselines despite operating on compressed representations.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18659
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/apple/ml-clara
[2] LLM Reasoning for Cold-Start Item Recommendation
This paper from Netflix tackles cold-start item recommendation by leveraging the reasoning capabilities of LLMs to infer user preferences for newly launched content with minimal interaction history. The authors propose two reasoning strategies:
Structural Reasoning, which systematically decomposes user viewing history into distinct reasoning paths based on preference factors (actors, genres, directors), computes match scores for each path against candidate items, and aggregates these scores using importance weights.
Soft Self-Consistency, a simpler variant that allows the LLM to autonomously construct diverse reasoning paths and synthesize them into final recommendations.
Beyond evaluating these zero-shot reasoning approaches, the study comprehensively investigates fine-tuning methodologies, including supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on successful reasoning trajectories, reinforcement learning fine-tuning using GRPO with reward functions based on recommendation accuracy, and hybrid SFT+GRPO combinations. Experiments on real-world Netflix data using Qwen-2.5-32B-Instruct demonstrate that the SFT and GRPO combination excels in warm-start settings, outperforming Netflix’s production ranking model by up to 8% on Discovery despite training on orders of magnitude fewer samples (thousands versus hundreds of millions).
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18261
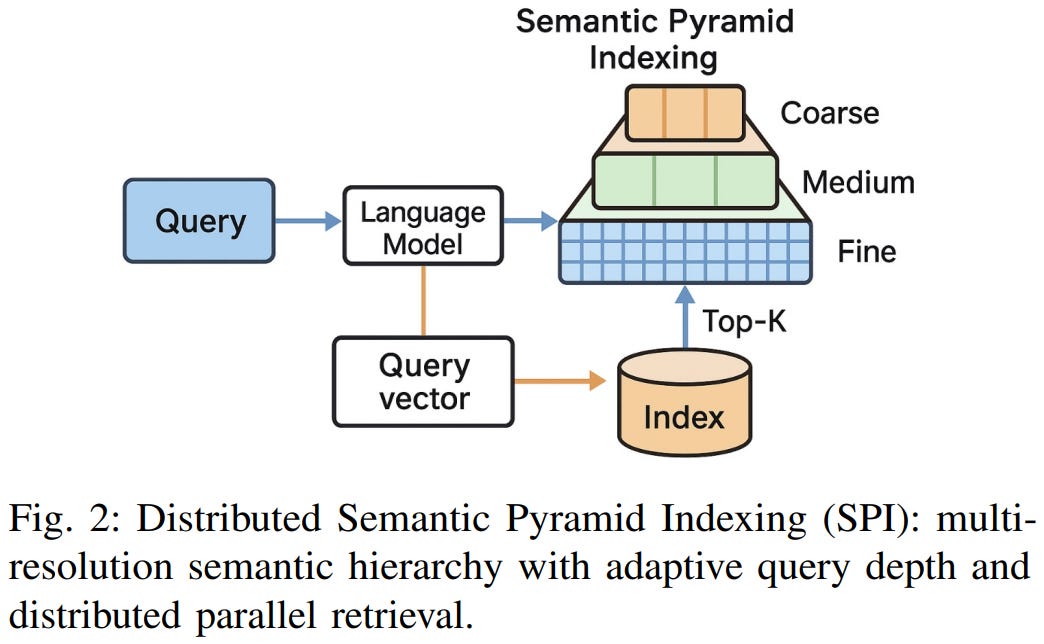
[3] Towards Hyper-Efficient RAG Systems in VecDBs: Distributed Parallel Multi-Resolution Vector Search
This paper from Liu et al. presents Semantic Pyramid Indexing (SPI), a multi-resolution vector indexing framework designed to improve efficiency in RAG systems. The authors address a key limitation of existing vector databases: single-resolution indexing that cannot adapt to queries of varying semantic complexity. SPI constructs a hierarchical “semantic pyramid” with multiple resolution levels, where document embeddings are progressively refined from coarse to fine representations. A lightweight classifier dynamically selects the optimal resolution level per query, enabling the system to handle simple queries at coarse levels while processing complex queries through deeper, more precise layers. Implemented as a plugin for FAISS and Qdrant, SPI demonstrates significant performance improvements across MS MARCO, Natural Questions, and multimodal LAION-5B benchmarks, achieving up to 5.7x speedup in retrieval latency and 1.8x memory efficiency while improving end-to-end QA F1 scores by 2.5 points. The framework includes theoretical guarantees on recall preservation and semantic consistency across resolution transitions, scales near-linearly across distributed nodes, and handles multimodal retrieval with cross-modal alignment mechanisms, though it incurs approximately 2.96x storage overhead compared to single-resolution baselines.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.16681
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/FastLM/SPI_VecDB
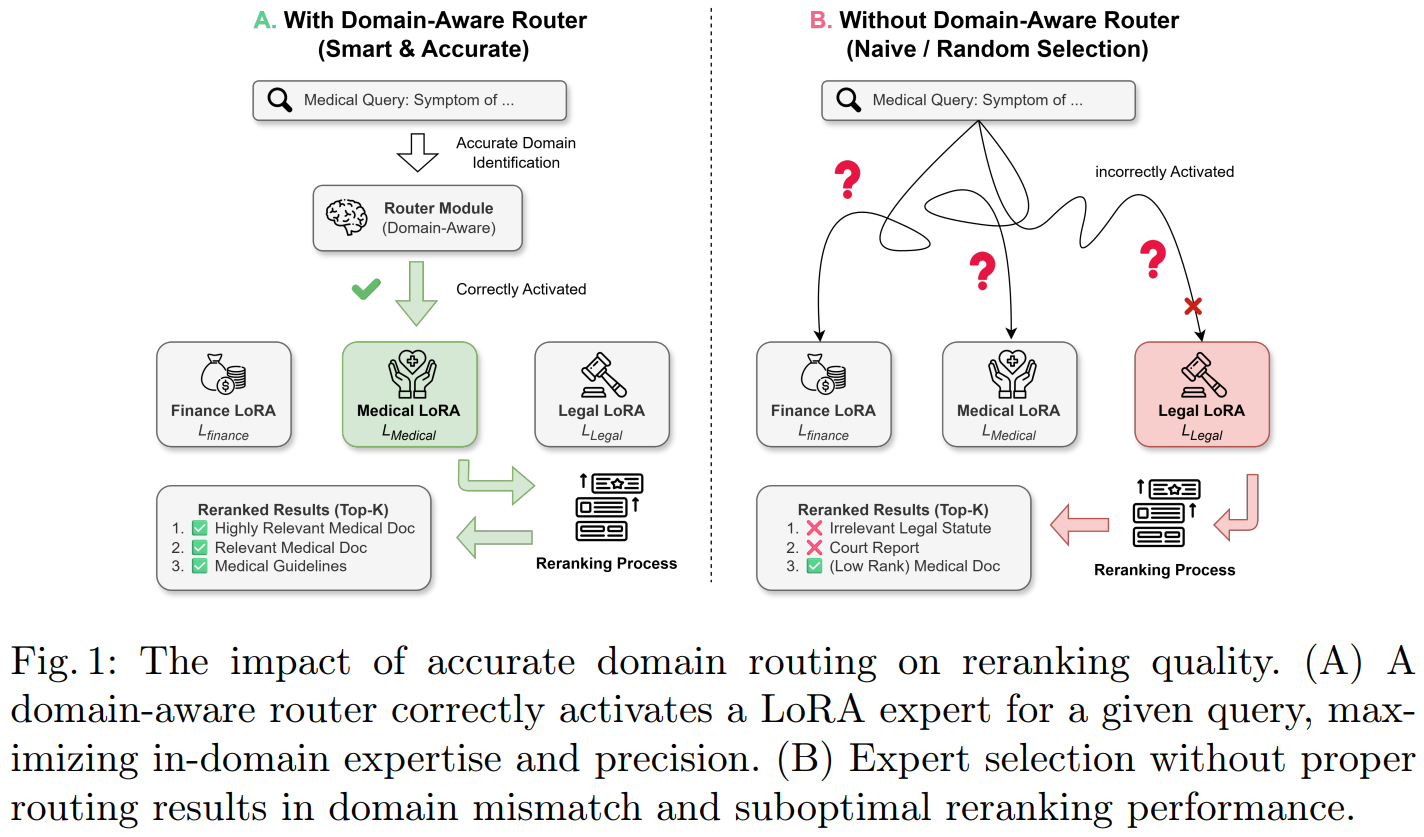
[4] R²R: A Route-to-Rerank Post-Training Framework for Multi-Domain Decoder-Only Rerankers
This paper from Wang et al. introduces Route-to-Rerank (R²R), a domain-adaptive framework for decoder-only rerankers in RAG systems that addresses the limitations of generalist models in specialized domains like finance, law, and medicine. The core innovation lies in a two-stage training strategy called Entity Abstraction for Generalization (EAG), which first trains on entity-masked data to prevent surface-form overfitting and learn domain-invariant relevance patterns, then fine-tunes on original domain-specific data to inject specialized knowledge while avoiding catastrophic forgetting. During inference, a lightweight Latent Semantic Router probes the frozen reranker backbone’s internal representations to dynamically select the optimal LoRA expert for each query, eliminating the need for external classifiers. Experiments across legal (LexRAG), medical (ChatDoctor), and other domain benchmarks using both Qwen3-Reranker and BGE-Reranker backbones demonstrate that R²R consistently outperforms both generalist baselines and naive domain fine-tuning approaches, while maintaining cross-domain robustness with minimal parameter overhead (0.2B additional parameters compared to 685B for LLM-based routing).
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19987
[5] Revisiting Feedback Models for HyDE
This paper from the University of Waterloo investigates whether traditional pseudo-relevance feedback models like Rocchio and RM3 can improve HyDE, a method that uses LLMs to generate hypothetical answer documents for query expansion in information retrieval. The authors observe that while classical feedback approaches employ sophisticated two-phase processes for selecting and weighting expansion terms, recent LLM-based methods like HyDE typically just concatenate the query with generated text. Through systematic experiments across 14 datasets (MS MARCO and BEIR benchmarks), they demonstrate that applying traditional feedback algorithms to HyDE-generated documents yields substantial improvements: up to 1.4 points (4.2%) on average, with 2.2 points (6%) on low-resource tasks, compared to string concatenation baselines. Notably, feedback models show greater robustness on diverse low-resource BEIR tasks compared to concatenation methods, and applying these models to LLM-generated documents consistently outperforms applying them to BM25-retrieved documents. The findings suggest that the extensive literature on feedback models remains highly relevant for modern LLM-based retrieval methods and should not be overlooked.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19349
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/nourj98/hyde-feedback
[6] NVIDIA Nemotron Parse 1.1
This paper from NVIDIA introduces Nemotron-Parse-1.1, an 885M-parameter encoder-decoder model for document parsing and OCR that improves upon its predecessor Nemoretriever-Parse-1.0 across multiple dimensions including general OCR, markdown formatting, table extraction, and text extraction from visual elements like charts and diagrams. The architecture employs a ViT-H/16-based vision encoder (657M parameters) initialized from RADIO and a compact 256M-parameter mBART-based decoder, with a novel design choice of omitting positional embeddings in the decoder to enable better generalization to longer sequences. The model supports flexible output through prompt-based control, allowing users to request formatted text (markdown/LaTeX), bounding boxes, and semantic class labels in various combinations. Trained on a diverse mixture of 22+ million samples including a newly developed NVpdftex synthetic dataset, public benchmarks, and human-annotated data across multiple languages, Nemotron-Parse-1.1 achieves competitive performance on standard benchmarks, notably excelling at table extraction and reading order prediction. The authors also release Nemotron-Parse-1.1-TC, a token-compressed variant that reduces vision sequence length by 16x (to 833 tokens) through pixel-shuffle operations, delivering approximately 20% faster inference with minimal accuracy degradation.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.20478
🤗 https://huggingface.co/nvidia/NVIDIA-Nemotron-Parse-v1.1
🤗 https://huggingface.co/nvidia/NVIDIA-Nemotron-Parse-v1.1-TC
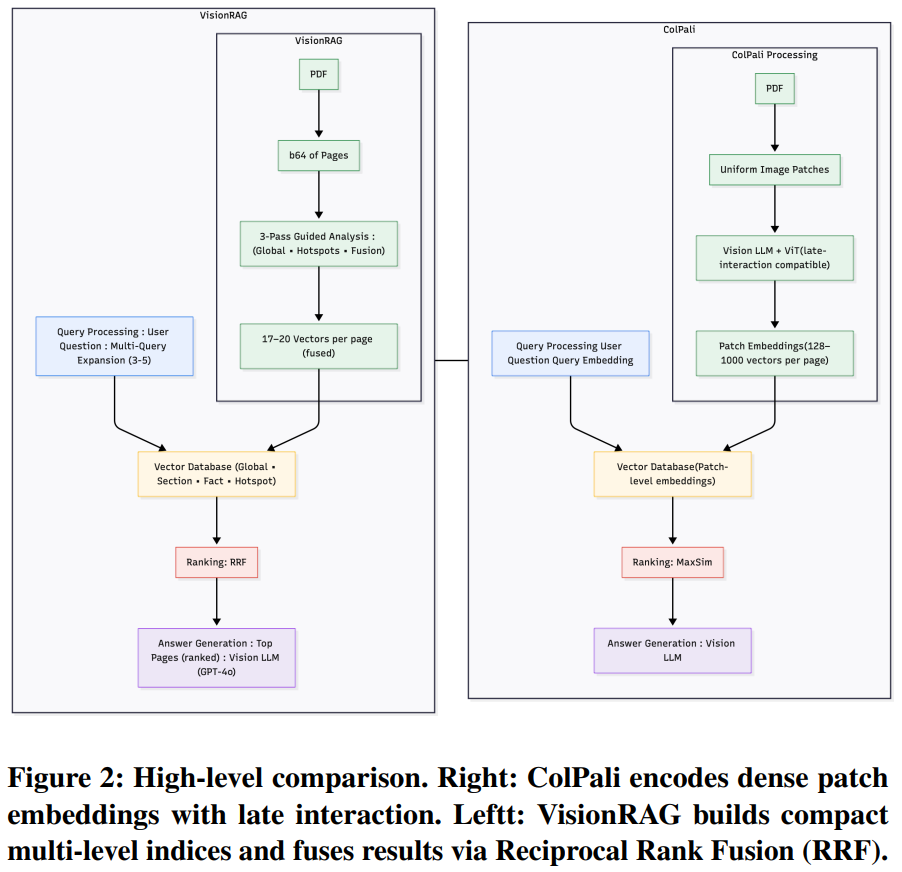
[7] Beyond Patch Aggregation: 3-Pass Pyramid Indexing for Vision-Enhanced Document Retrieval
This paper from Inception AI introduces VisionRAG, an OCR-free document retrieval system designed to address the computational inefficiencies of existing vision-based retrieval methods like ColPali. While ColPali processes document pages as images and generates dense patch-level embeddings (1024 vectors per page), VisionRAG employs a “3-pass pyramid indexing” approach that extracts semantic information at multiple granularities: global page summaries, section headers, key facts, and visual hotspots. This results in only 17-27 compact vectors per page compared to ColPali’s hundreds, achieving substantial memory savings (6-9x reduction) while maintaining comparable retrieval performance. The system uses vision-language models (primarily GPT-4o) to analyze page images and generate semantic artifacts, which are then embedded and indexed separately. At query time, VisionRAG retrieves relevant pages using Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) across multiple indices and query variants, then forwards the raw page images to a multimodal LLM for answer generation. Experiments demonstrate that VisionRAG provides a production-ready alternative to patch-based vision retrieval with significantly lower infrastructure requirements and faster query processing times (10-14ms vs. 42-65ms for ColPali).
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.21121
[8] Generative Early Stage Ranking
This paper from Meta introduces Generative Early Stage Ranking (GESR), an architecture designed to enhance the effectiveness of Early Stage Ranking (ESR) systems in large-scale recommendation pipelines while maintaining computational efficiency. Traditional ESR models employ a “Two Tower” user-item decoupling approach that, while computationally efficient through precomputed item embeddings, fails to capture fine-grained user-item interactions and cross-signals. GESR addresses this limitation by augmenting the Two Tower architecture with a Mixture of Attention (MoA) module that incorporates three complementary attention mechanisms: Hard Matching Attention (HMA) computes explicit cross-signals through raw feature overlap counts; Target-Aware Self Attention leverages HSTU-based sequential modeling to generate implicit, target-conditioned user representations; and RO/NRO Cross Attention modules enable symmetric user-item contextualization while scaling linearly with sequence length. These enriched representations are then refined through Multi-Logit Parameterized Gating (MLPG), which performs parallel logit computations with dynamic gating to amplify the most informative signals. To address the computational challenges of deploying target-aware attention at ESR scale, the authors implement comprehensive optimizations, including FP8 quantization, custom kernels, tensor memory optimization, and efficient caching strategies.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.21095
[9] E2E-GRec: An End-to-End Joint Training Framework for Graph Neural Networks and Recommender Systems
This paper from TikTok introduces E2E-GRec, an end-to-end joint training framework that integrates Graph Neural Networks with industrial recommender systems. The framework addresses two critical problems: the high computational overhead of repeatedly executing offline GNN inference to refresh embeddings, and the lack of joint optimization where recommendation gradients cannot influence GNN learning. The proposed solution incorporates three key components: efficient subgraph sampling from large-scale cross-domain heterogeneous graphs using importance sampling, a Graph Feature Auto-Encoder (GFAE) that serves as a self-supervised auxiliary task to guide GNN learning toward structurally meaningful embeddings, and a two-level feature fusion mechanism combined with Gradnorm-based dynamic loss balancing to enable stable multi-task end-to-end training. The authors provide theoretical analysis demonstrating why end-to-end training yields more informative embeddings than cascaded approaches, proving that the gradient coupling enables both GNN-to-recommendation and recommendation-to-GNN optimization flows. Extensive experiments on TikTok’s production system demonstrate significant improvements, including a +0.133% relative increase in stay duration and a -0.3171% reduction in video skips.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.20564
[10] STORE: Semantic Tokenization, Orthogonal Rotation and Efficient Attention for Scaling Up Ranking Models
This paper from Alibaba presents STORE to address fundamental scalability challenges in ranking models for recommender systems by tackling two bottlenecks: the representation bottleneck caused by high-cardinality sparse features forcing model capacity into sparse-activated embeddings (leading to low-rank representations and phenomena like “One-Epoch” and “Interaction-Collapse”), and the computational bottleneck arising from the explosion of feature tokens when integrating heterogeneous features. The framework introduces three main innovations:
Semantic Tokenization, which decomposes high-cardinality sparse features into compact semantic tokens using an Orthogonal, Parallel, Multi-expert Quantization network (OPMQ) that maps item IDs into stable Semantic IDs through vector quantization of pre-trained embeddings.
Orthogonal Rotation Transformation, which applies learned orthogonal matrices to rotate low-cardinality static features into diverse high-dimensional spaces to facilitate more effective feature interactions while maintaining orthogonality constraints through diversity regularization.
Efficient Attention mechanism that employs a routing strategy to reduce computational complexity from O(L²) to linear by having each query attend only to selected key-value blocks rather than all tokens.
Experiments demonstrate substantial improvements, with online A/B tests showing a 2.71% relative increase in CTR, 1.195% improvement in AUC, and 1.84x higher training throughput compared to state-of-the-art baselines, including RankMixer and OneTrans.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18805
Extras: Benchmarks
⏱️ E-GEO: A Testbed for Generative Engine Optimization in E-Commerce
E-GEO is a benchmark designed to study generative engine optimization (GEO) in e-commerce settings, where LLMs increasingly act as re-ranking systems for product recommendations. The benchmark consists of more than 7,000 long, intent-rich consumer product queries sourced from Reddit and paired with relevant Amazon listings, capturing the detailed preferences and constraints common in conversational shopping.
📝 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.20867
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/psbagga17/E-GEO
I hope this weekly roundup of top papers has provided you with valuable insights and a glimpse into the exciting advancements taking place in the field. Remember to look deeper into the papers that pique your interest.
I also blog about Machine Learning, Deep Learning, MLOps, and Software Engineering domains. I explore diverse topics, such as Natural Language Processing, Large Language Models, Recommendation Systems, etc., and conduct in-depth analyses, drawing insights from the latest research papers.