A GPU-Native Framework for Billion-Scale Recommendation, Efficient Document Reranking Through Group-Level Scoring, and More!
Vol.131 for Nov 17 - Nov 23, 2025
Stay Ahead of the Curve with the Latest Advancements and Discoveries in Information Retrieval.
This week’s newsletter highlights the following research:
SilverTorch: A Unified GPU Architecture for Large-Scale Recommendation Systems, from Meta
Bridging Pointwise Flexibility and Listwise Performance in Neural Reranking, from Ant Group
Efficient Bilingual Text Embedding via Multi-Teacher Distillation and Dynamic Token Compression, from Zhang et al.
Enhancing ColBERT with Token-Level Importance Weighting for Improved Retrieval, from Microsoft Research
Learning Disentangled User Interests for Robust CTR Prediction Under Distribution Shift, from Zheng et al.
Training-Free Bias Correction in Text Embeddings, from Ren et al.
A Reinforcement Learning Framework for Multi-Objective Dense Retrieval without Hard Negative Mining, from Alibaba
Unified Training of Multimodal Encoders and Ranking Models for Large-Scale Recommendation, from ByteDance
Cost-Effective Neural Pre-Ranking via Asynchronous Feature Computation, from Alibaba
A Comprehensive Survey of Graph-Based Retrieval-Augmented Generation, from Peng et al.
[1] SilverTorch: A Unified Model-based System to Democratize Large-Scale Recommendation on GPU
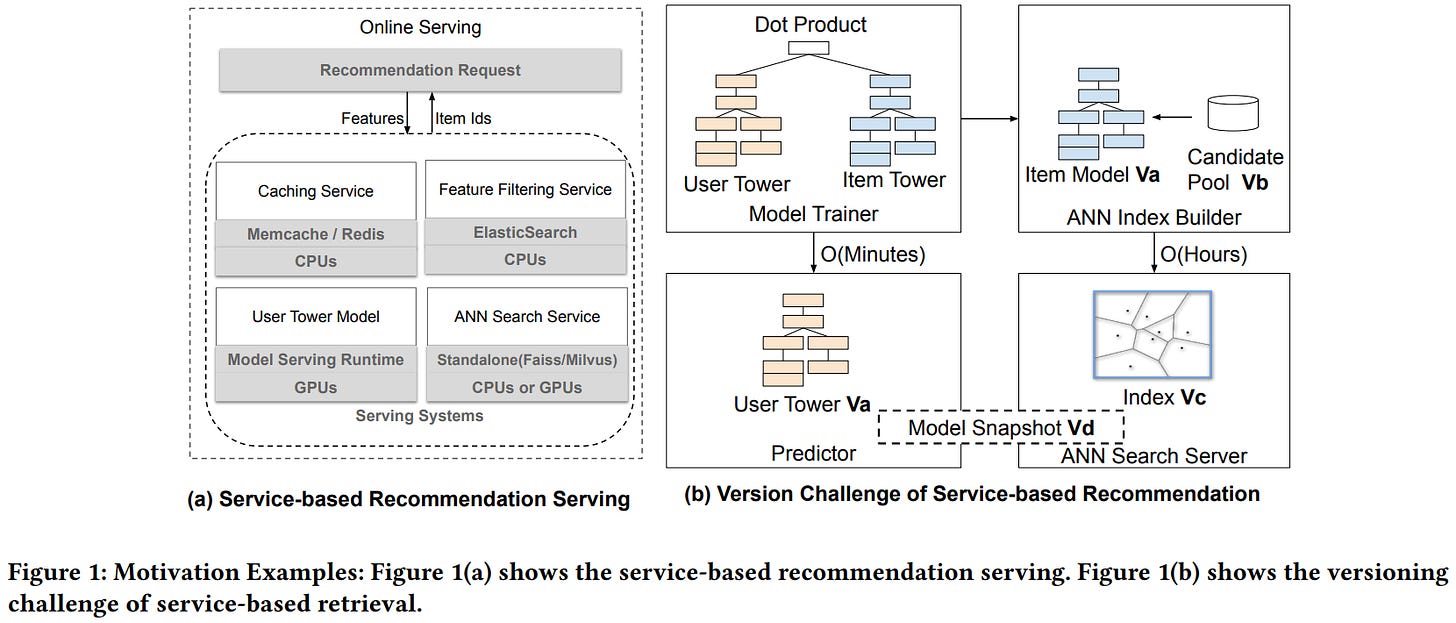
This paper from Meta presents SilverTorch, a unified GPU-based system for serving large-scale recommendation models that addresses inefficiencies in traditional service-based architectures. Existing recommendation systems rely on separate CPU-based services for ANN indexing, feature filtering, and caching, creating version inconsistency issues, communication overhead, and limited support for complex model architectures like learned similarities and multi-task retrieval. SilverTorch reimagines these components as layers within a single PyTorch model served on GPUs, introducing two key innovations: a novel Bloom index algorithm for GPU-based feature filtering that uses signature-based bit operations to process 64 items simultaneously, and a fused Int8 quantized ANN kernel that enables searching arbitrary topk values with reduced memory footprint. The system further co-designs these indexes to eliminate unnecessary computation and memory allocation, achieving a 30x reduction in feature filtering compute for partial candidate sets. By unifying the serving stack, SilverTorch enables advanced capabilities, including OverArch scoring layers for learned user-item interactions, multi-task retrieval with in-model value aggregation, and embedding caching for early-stage ranking that pre-loads item embeddings into GPU memory. Experiments on industry-scale datasets with 10-80 million items demonstrate that SilverTorch achieves 23.7x higher throughput, 5.6x lower latency, and 13.35x better cost-efficiency compared to CPU-based baselines, while improving recall by over 5.6% through its support for more complex model architectures, and currently serves billions of daily active users across major products at Meta.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.14881
[2] GroupRank: A Groupwise Reranking Paradigm Driven by Reinforcement Learning
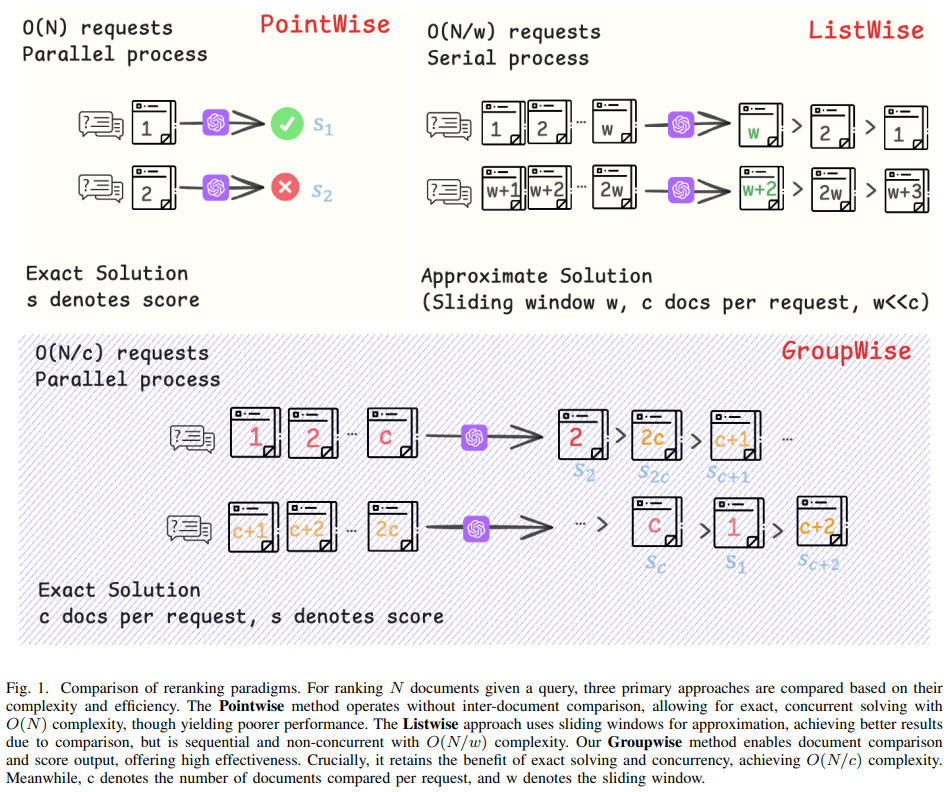
This paper from Ant Group introduces GroupRank, a reranking paradigm for RAG systems. Traditional pointwise methods suffer from “ranking myopia” because they evaluate documents independently without global context, while listwise methods face “list rigidity” issues when handling large candidate sets. GroupRank resolves this by jointly scoring groups of documents in a single forward pass, enabling inter-document comparisons while maintaining the flexibility to process arbitrary numbers of candidates with O(N/c) complexity. The authors employ a two-stage training strategy: supervised fine-tuning followed by reinforcement learning using GRPO with a heterogeneous reward function that combines ranking metrics (NDCG, Recall, RBO) with a distributional reward for score alignment. To address data scarcity, they develop a synthetic data pipeline that generates high-quality training examples by fusing pointwise LLM scores with listwise rankings.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.11653
🤗 https://huggingface.co/AQ-MedAI/Diver-GroupRank-7B
[3] Jasper-Token-Compression-600M Technical Report
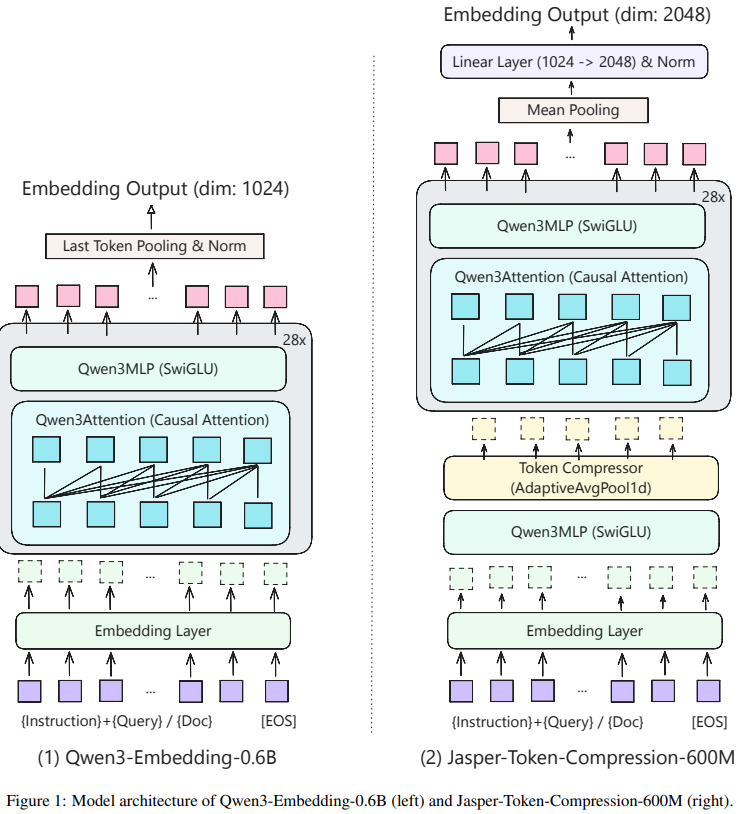
This technical report from Zhang et al. introduces Jasper-Token-Compression-600M, a bilingual (English-Chinese) text embedding model that achieves performance comparable to 8B models while maintaining the efficiency of a 600M parameter model through innovative token compression techniques. The model employs a four-stage training methodology: (1) knowledge distillation from two complementary teacher models (Qwen3-Embedding-8B and QZhou-Embedding-7B), (2) integration of a one-dimensional convolution-based token compression module using AdaptiveAvgPool1d, (3) dynamic compression ratio training that samples different compression rates (0.1 to 1.0) to enable flexible inference-time compression, and (4) contrastive learning to enhance retrieval capabilities. The token compression module significantly reduces sequence length before the attention mechanism, yielding substantial efficiency gains. The model achieves Mean Task scores of 74.75 on English MTEB and 73.51 on Chinese MTEB benchmarks, demonstrating that strategic architectural modifications and multi-teacher distillation can produce compact models that rival much larger counterparts in both performance and practical deployment scenarios.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.14405
🤗 https://huggingface.co/infgrad/Jasper-Token-Compression-600M
[4] Incorporating Token Importance in Multi-Vector Retrieval
This paper from Microsoft Research introduces Weighted Chamfer, an enhancement to ColBERT’s late interaction mechanism that incorporates token importance weights into multi-vector retrieval. While ColBERT computes query-document similarity by summing the minimum distances between query tokens and document tokens uniformly, Weighted Chamfer applies learned weights to each query token’s contribution, capturing relative token importance analogous to term weighting in BM25. The authors demonstrate that this modification only requires training token weights while keeping the pre-computed multi-vector document representations fixed and significantly improves retrieval performance with minimal computational overhead. In zero-shot settings, using IDF-based weights derived solely from corpus statistics, the method achieves an average improvement of 1.28% in Recall@10 across the BEIR benchmark. The approach is particularly valuable for low-resource scenarios where full model fine-tuning is impractical, as it requires training only O(vocabulary size) parameters rather than the entire encoder.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.16106
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/kayalneeraj/weighted_chamfer
[5] Disentangled Interest Network for Out-of-Distribution CTR Prediction
This paper from Zheng et al. introduces DiseCTR, a click-through rate prediction model designed to address the out-of-distribution (OOD) problem in recommender systems where training and test data distributions differ due to evolving user interests. The authors observe that existing CTR models suffer significant performance degradation in OOD scenarios because they directly learn P(Y|X) without considering that users have multiple unobserved interests that change partially over time. DiseCTR takes a causal inference approach by factorizing CTR prediction into interest model P(Z), exposure model P(X|Z), and click model P(Y|X,Z), then separately learning P(Z|X) and P(Y|Z) through three key components: (1) an interest encoder using sparse attention to map features to interest embeddings, (2) an interest disentangler that clusters embeddings to prototypes and applies pairwise weak supervision to ensure interests are both meaningful and independent, and (3) an attentive interest aggregator that combines disentangled interests for prediction. By disentangling user interests, DiseCTR leverages the partial-distribution-variation property where only a few interests change while others remain stable, making the model more robust to distribution shifts.
📚 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3777368
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/DavyMorgan/DiseCTR/
[6] Correcting Mean Bias in Text Embeddings: A Refined Renormalization with Training-Free Improvements on MMTEB
This paper from Ren et al. identifies a systematic mean bias in text embedding models, where each embedding vector can be decomposed as e = ẽ + μ, with μ being a nearly constant vector across all sentences that represents anisotropy rather than meaningful semantic information. The authors propose renormalization, a plug-and-play, training-free solution involving two variants: R1 (directly subtracting μ) and R2 (removing the projection of e onto μ). Through theoretical analysis based on error propagation, they predict R2 should outperform R1 because it better cancels estimation errors in the parallel component while retaining less orthogonal noise. Extensive experiments across 38 models on the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB) validate this prediction, showing that renormalization achieves statistically significant improvements of 9.7σ on retrieval tasks, 3.1σ on classification tasks, and 0.8σ on other task types. The effectiveness correlates positively with the magnitude of the mean vector norm, supporting the anisotropy explanation. The method’s simplicity, computational efficiency, and consistent improvements make it a practical post-processing technique applicable to existing embedding models without retraining.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.11041
[7] TaoSearchEmb: A Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning Framework for Dense Retrieval in Taobao Search
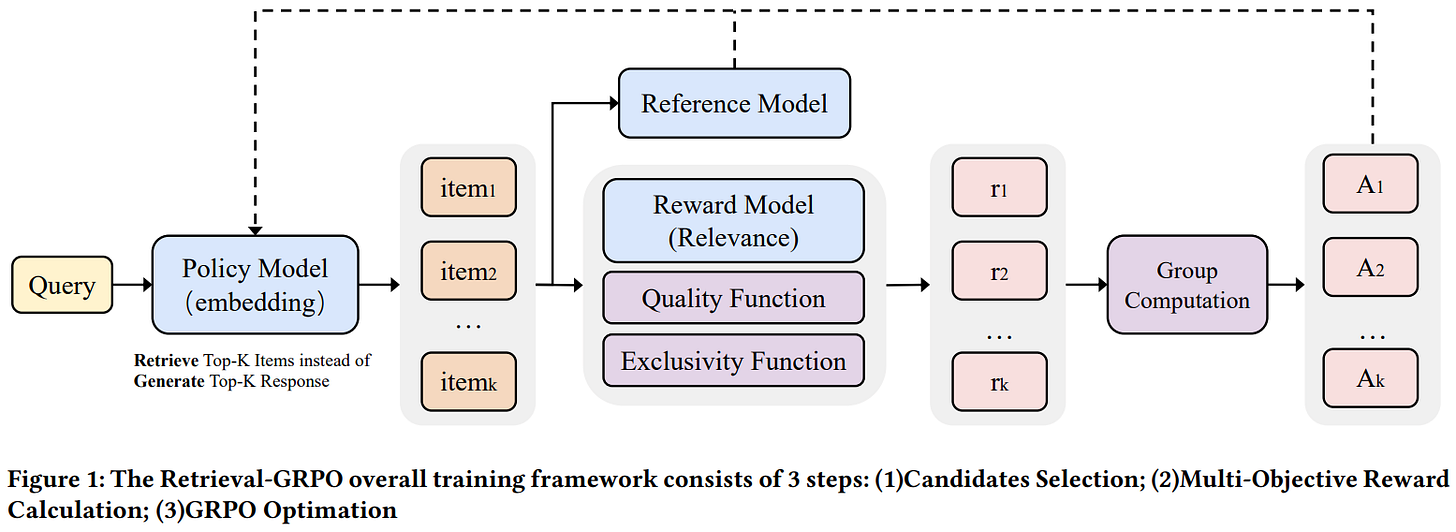
This paper from Alibaba introduces TaoSearchEmb, a multi-objective reinforcement learning framework for dense retrieval in Taobao’s e-commerce search system. The authors propose Retrieval-GRPO, which eliminates the need for labor-intensive offline hard negative sample mining by dynamically retrieving top-k candidate items during training and using a 42B-parameter relevance LLM (TaoSR1) as a reward model to provide real-time feedback. The framework optimizes embeddings through a multi-objective reward function that combines relevance scores, item quality metrics, and exclusivity measures (to reduce overlap with inverted-index retrieval), effectively mitigating the seesaw effect common in multi-task learning. The training pipeline consists of two stages: supervised fine-tuning with enhanced negative sampling (combining in-batch and global negatives), followed by Retrieval-GRPO optimization using group-based advantage estimation. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements over baselines, particularly on challenging long-tail queries including negations, alternatives, Q&A, and knowledge-based searches.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.13885
[8] LEMUR: Large scale End-to-end MUltimodal Recommendation
This paper from ByteDance introduces LEMUR, a large-scale end-to-end multimodal recommendation system deployed in production, specifically on Douyin (the Chinese version of TikTok). Unlike conventional two-stage approaches that pretrain multimodal models separately and use frozen representations for downstream recommendation tasks, LEMUR jointly optimizes both multimodal encoders and ranking models in a unified training framework. The system addresses the computational bottleneck of processing multimodal sequential representations through a novel memory bank mechanism that incrementally stores and retrieves historical multimodal embeddings from a parameter server, eliminating expensive online transmission costs. LEMUR employs a session-masked query-document contrastive (SQDC) loss to align query and document representations, incorporates quality and exclusivity rewards alongside relevance scores, and utilizes sampling strategies and cross-worker deduplication to improve training efficiency.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.10962
[9] AIF: Asynchronous Inference Framework for Cost-Effective Pre-Ranking
This paper from Alibaba introduces the Asynchronous Inference Framework (AIF), a computational architecture designed to optimize pre-ranking models in industrial recommendation systems. The authors identify inefficiencies in traditional sequential inference pipelines, including redundant computations of identical user/item features across mini-batches and increased latency from strictly sequential operations. AIF addresses these limitations by decoupling interaction-independent components (user-side and item-side computations) from real-time prediction, executing user-side computations in parallel with retrieval and performing item-side computations in a nearline manner. The framework implements three key strategies: asynchronous online inference for user features during retrieval, nearline asynchronous inference for item features with update-triggered execution, and pre-caching mechanisms for cross-features. For interaction-dependent components that cannot be fully asynchronized, the authors propose approximation methods, including Bridge Embedding Approximation (BEA) for efficient dimensionality expansion and Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH) for long-term user behavior modeling with reduced computational complexity. Deployed in Taobao’s display advertising system, AIF achieved substantial improvements of +8.72% in click-through rate and +5.80% in revenue per mille, with negligible latency increase and less than 15% computational overhead.
📚 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.12934
[10] Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey
This paper from Peng et al. presents a comprehensive survey of Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG), an emerging paradigm that leverages structured graph data to enhance LLM responses. While conventional RAG methods retrieve isolated text chunks based on semantic similarity and often suffer from redundant information and inability to capture complex relational knowledge, GraphRAG explicitly models entity relationships through graph structures, enabling more precise multi-hop reasoning and comprehensive information retrieval. The authors formalize the GraphRAG workflow into three core stages: Graph-Based Indexing (constructing and organizing graph databases from open knowledge graphs or self-constructed data), Graph-Guided Retrieval (extracting relevant graph elements like nodes, triplets, paths, or subgraphs using non-parametric, LM-based, or GNN-based retrievers), and Graph-Enhanced Generation (converting retrieved graph structures into formats processable by language models). The survey systematically categorizes existing methodologies across these stages, examines retrieval paradigms (once, iterative, and multi-stage), discusses training strategies, and analyzes downstream applications spanning question answering, recommendation systems, and domain-specific tasks in healthcare, finance, and e-commerce.
📚 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3777378
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/pengboci/GraphRAG-Survey
Extras: Datasets
💾 RAGPulse: An Open-Source RAG Workload Trace to Optimize RAG Serving Systems
RAGPulse is a dataset collected from a university-wide RAG-based policy Q&A system that has served over 40,000 users since April 2024. The dataset contains 7,106 anonymized request records sampled over one week, capturing system-level information such as timestamps, input and output token lengths, hashed identifiers for all input components, and session metadata.
📝 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.12979
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/flashserve/RAGPulse
Extras: Benchmarks
⏱️ NeuCLIRBench: A Modern Evaluation Collection for Monolingual, Cross-Language, and Multilingual Information Retrieval
NeuCLIRBench is a large-scale benchmark designed to evaluate monolingual, cross-language, and multilingual retrieval systems using a unified collection of news documents in Chinese, Persian, and Russian, along with their machine-translated English versions. It combines three years of TREC NeuCLIR topics (2022–2024) and provides over 10 million documents, manually translated queries, and 250k relevance judgments, offering strong statistical power across multiple retrieval scenarios. The benchmark includes deep human judgments for each query and a fused baseline built from modern neural retrievers.
📝 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.1475
🤗 https://huggingface.co/datasets/neuclir/bench
💾 LiveRAG: A diverse Q&A dataset with varying difficulty level for RAG evaluation
LiveRAG is a benchmark of 895 synthetic question–answer pairs derived from the SIGIR 2025 LiveRAG Challenge, designed to support systematic evaluation of RAG systems. Built using the DataMorgana generation pipeline, it combines questions from two challenge sessions and augments them with reference answers, supporting documents, and the “answer claims” used for evaluation. Each question is also associated with difficulty and discriminability scores. The benchmark spans diverse question types and linguistic variations.
📝 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.14531
🤗 https://huggingface.co/datasets/LiveRAG/Benchmark
Extras: Tools
💾 QueryGym: A Toolkit for Reproducible LLM-Based Query Reformulation
QueryGym is a lightweight, extensible Python toolkit presented to support LLM-based query reformulation. The toolkit includes a Python API for applying diverse LLM-based methods, a retrieval-agnostic interface supporting integration with backends like Pyserini and PyTerrier, a centralized prompt management system, and built-in support for benchmarks such as BEIR and MS MARCO. The core capabilities are structured around a unified reformulation framework, a retrieval-agnostic interface, a centralized prompt bank, and LLM compatibility and reproducibility support.
📝 https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.15996
👨🏽💻 https://github.com/radinhamidi/QueryGym
I hope this weekly roundup of top papers has provided you with valuable insights and a glimpse into the exciting advancements taking place in the field. Remember to look deeper into the papers that pique your interest.
I also blog about Machine Learning, Deep Learning, MLOps, and Software Engineering domains. I explore diverse topics, such as Natural Language Processing, Large Language Models, Recommendation Systems, etc., and conduct in-depth analyses, drawing insights from the latest research papers.